Blockchain uses a distributed ledger technology system designed to drive transparency and trust, which are essential across a number of enterprise business applications. Blockchain solutions enable businesses to process payments and validate digital identities more securely and transparently than legacy technologies.
Business runs on data, and blockchain technology offers improved methods for data stewardship and management. Using blockchain, organizations can achieve stronger efficiency and security across a wide range of business applications. Below, we’ll dive into specific areas where we see enterprise use cases for blockchain, detailing the ways in which the technology can improve business operations.
How Does Blockchain Work?
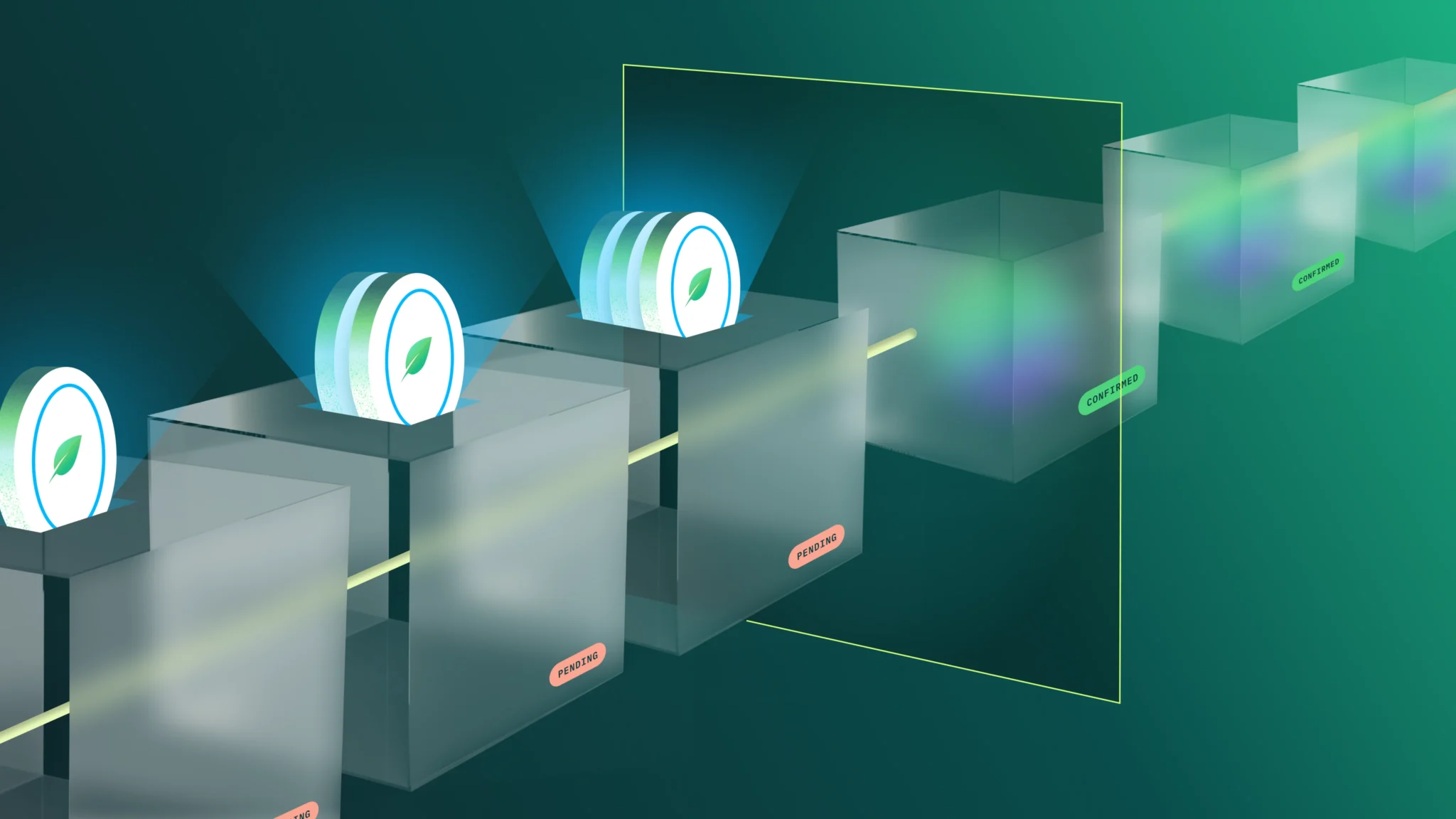
A blockchain is a distributed system used to record transactions across a network of computers called “nodes.”
Data is stored in “blocks” which reach a data capacity and then “chain” to another “block” to create an unbroken and immutable system of record. Thus, the “blockchain” is a distributed and immutable data network accessible to all transactors in an ecosystem.
However, many “enterprise-specific” or colloquially, private, blockchains are “permissioned.” The entity that owns the blockchain exerts a degree of control over who has access to the ledger and which types of transactions may be processed. This is a potentially risky prospect to those users without control, and inherently incompatible with the primary values of auditability and transparency that make blockchain technology an innovative solution for data stewardship.
Public blockchains differ dramatically from private blockchains. They are an entirely decentralized network of nodes managed by people unknown to each other. Thus, they are not under the control of any one entity, for example, the Chia blockchain is public. Public blockchains offer enhanced transparency and immutability of the ledger through decentralizing the control of the blockchain to the vast network of nodes, but transactions on the blockchain typically remain publicly viewable.
There can be benefits and drawbacks to using one or the other, and an organization should understand its needs and goals for the technology’s use in their specific case.
Today’s Applications of Blockchain for Enterprise
Today, blockchain is most commonly associated with the technology’s applications within the financial sector. While blockchain can be advantageous to financial services firms, aiding in transactions like real-time payments, the technology’s applications and benefits are widespread across industries.
For example, blockchain-enabled supply chains can make businesses more efficient by ensuring that products reach customers at a quicker rate. This increases product traceability, and leads to smoother coordination between the business and its suppliers.
Blockchain-enabled supply chains can also aid businesses in managing supply chain risk, protecting each step of a product’s journey from production to the customer by marking and storing each transaction on an immutable ledger. U.S.-based defense contractor Lockheed Martin was the first company of its kind to implement a blockchain-enabled supply chain solution in its product development. As part of a partnership with SyncFab, Lockheed Martin now has direct access to a parts procurement and supply chain platform built on SyncFab’s blockchain.
Lockheed Martin is not the only business adopting this technology – according to Cointelegraph, over half of the companies on the Forbes Blockchain 50 list in 2021 used blockchain to solve logistical issues.
One such industry primed for enterprise blockchain is healthcare. Blockchain-enabled healthcare can improve how providers maintain client records, process transactions, and manage risk – ultimately, lowering costs, enhancing patient and clinical experiences, and increasing efficiency in a secure way.
By storing patient data on a permissioned, private blockchain, healthcare providers ensure that highly sensitive data, like electronic healthcare records, remain confidential. In this way, the secure and auditable nature of blockchain technology protects patient privacy, while creating data management efficiencies to advance healthcare practices.
Blockchain for Enterprise Examples
As awareness and adoption of enterprise blockchain use cases continue to grow, we at Chia see six primary areas of opportunity for blockchain to provide real-world business solutions. Within this scope lies applications across blockchain-enabled markets and blockchain security.
Chia’s work with the Climate Action Data (“CAD”) Trust in partnership with the World Bank exhibits blockchain’s utility for markets. The CAD Trust is an open-source metadata system that uses blockchain technology to create a decentralized record of carbon market activity with the goals of avoiding double-counting, increasing trust in carbon credit data, and building confidence in carbon markets through improved transparency. Unlike most enterprise blockchain applications, the CAD Trust operates on an open-source system fully accessible to the public. These features empower partners to trade digital assets (in this case, carbon credits) in a trustless ecosystem, strengthening markets through an inherently cross-border and cross-market blockchain.
Blockchain technology is designed to promote trust and confidence within an ecosystem. When it comes to security, blockchain offers a robust set of solutions for businesses and individuals with the potential to improve everything from identity and access management, data privacy, and more. Today, large financial institutions, like JPMorgan, are turning to blockchain for security solutions. The bank recently announced plans to partner with six Indian banks to settle interbank dollar transactions on a blockchain. Beyond improving the security of these transactions, the blockchain solution will also allow for real-time transactions, which previously took hours or days to complete under the old technological regime.
Future Blockchain Development
Blockchain software development remains nascent, but bridging the gap between private and public blockchains would offer enterprises a more secure solution while retaining the transparency and auditability blockchain technology affords. For example, Chia’s Virtual Private Blockchain (VPB) harnesses the transparency of the public blockchain while layering in the ability to add permissions and other benefits of private blockchains in a single solution.
We’re still only at the beginning of how this technology will be developed and deployed, but we believe the Chia Virtual Private Blockchain offers a novel path forward to protect enterprises and the data they’re storing.
FAQs
Q: What is blockchain for enterprise?
A: Blockchain for enterprise is a distributed ledger system designed to drive transparency and trust across numerous business applications. Using a distributed and immutable data network, blockchains can streamline operations, including transaction recording, payment processing, digital identity validation, and more in a secure ecosystem.
Q: How does blockchain work?
A: Blockchains store data on a distributed network in “blocks,” which reach a data capacity and then “chain” to another “block.”
Q: How is blockchain for enterprise different?
A: Blockchains leveraged by enterprises can be public or private based on their needs, but today, are more often private systems for the permissioning tools.
Q: What business outcomes can blockchain support?
A: The technology’s applications and benefits are widespread across industries, including sectors such as supply chain, insurance, and healthcare. Blockchain-enabled supply chains aid businesses in managing supply chain risk, protecting each step of a product’s journey from production to the customer by marking and storing each transaction on an immutable blockchain. Furthermore, blockchain technology can be used to improve how healthcare providers maintain client records, process transactions, and manage risk – ultimately, lowering costs, enhancing patient and clinical experiences, and increasing efficiency in a secure way.
Q: How is blockchain being adopted in the real-world?
A: As awareness and adoption of blockchain use cases continue to grow, so does the opportunity for it to provide real-world business solutions. Within this scope lies applications across blockchain-enabled markets and blockchain security. Chia’s work with the Climate Action Data (“CAD”) Trust in partnership with the World Bank exhibits blockchain’s utility for markets, empowering partners to trade digital assets (in this case, carbon credits) in a trustless ecosystem and strengthening markets through an inherently cross-border and cross-market blockchain. When it comes to security, blockchain offers a robust set of solutions for businesses and individuals with the potential to improve everything from identity and access management, data privacy, and more. Today, large financial institutions, like JPMorgan, are turning to blockchain for security solutions.