A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, also known as nodes. In other words, blockchain is a peer-to-peer digital network that collaborates to maintain a shared record of interactions. While today’s blockchains are most commonly associated with financial transactions, the technology’s potential use cases go far beyond finance.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
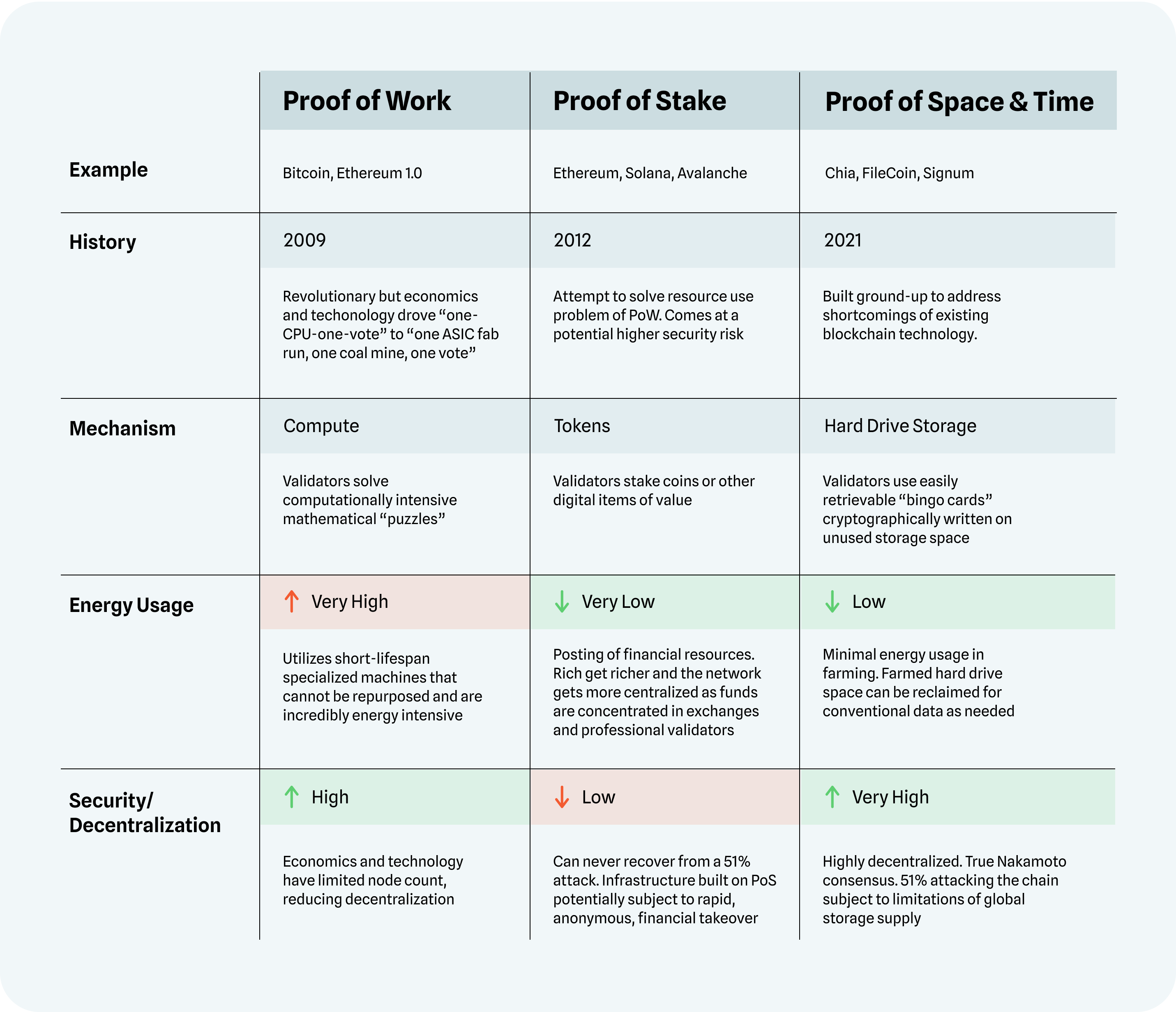
The fundamental operations of blockchains are inherent to its name. The basic way blockchains function is by packaging transactions into what is known as blocks. Following this, the new block is validated by network nodes through a consensus mechanism — adding to the ledger’s chain, thus the titling of “blockchain”. Some common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Proof of Space and Time.
Proof of Work
Proof of Work (PoW) is the consensus mechanism predominantly associated with the Bitcoin network and requires nodes to dedicate processing power to decrypt a transaction. The node which successfully solves the cryptographic puzzle associated with a given transaction is rewarded, and all other nodes incorporate the transaction on the overall ledger.
PoW, while secure, carries several drawbacks, specifically the large energy requirements to validate transactions and the high costs associated with obtaining a computer powerful enough to validate transactions successfully and receive rewards.
Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus mechanism commonly associated with the Ethereum network. Rather than requiring miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to verify transactions, PoS creates and validates transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Validators, who are individuals participating in the network, take turns creating and validating transactions based on their staked holdings, with rewards being divided up between them. PoS is significantly less energy intensive than PoW but is also far more centralized, resulting in criticisms that such a consensus mechanism runs contrary to the decentralized nature of blockchain technology and limits the resulting security.
Proof of Space and Time
Proof of Space and Time (PoST) is an emerging consensus mechanism pioneered by the Chia Network. PoST leverages unused hard drive storage capacity alongside time to reach consensus and validate transactions rather than the validators associated with PoS and the cryptographic puzzles related to PoW.
PoST uses storage rather than processing power to validate transactions, lowering energy costs and expanding the number of individuals who can validate transactions on the network. PoST maintains the decentralized nature of PoW while significantly reducing the energy used, combining the best of both worlds – the security and decentralization of PoW with the lower energy costs tied to PoS.
Blockchain Consensus Model Comparison
Blockchain Security through Transparency
So, why is blockchain important? Blockchain technology provides several distinct advantages over traditional means of transaction verification in today’s digital ecosystem. The decentralized nature of a blockchain means that no single entity has control over the entire system, making it secure and resistant to increasingly common tampering and cyber-attacks.
With the decentralized nature of blockchain also comes improved transparency by allowing individuals to view all transactions on a given blockchain. This transparency is especially critical in industries where trust is paramount, such as financial services, supply chain management, and healthcare. Lastly, blockchain allows for automated validation and verification of transactions, removing the need for intermediaries and making transactions faster and cheaper.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is primed to benefit a wide range of industries. While its application is not limited to any specific sector, several industries stand to gain significant advantages from blockchain technology’s broadening adoption, specifically financial services, healthcare, and real estate.
The financial services industry, particularly in digital transactions, faces numerous challenges that blockchain technology can address. The realm of payments and remittances represents a key area for blockchain’s substantial impact. By leveraging blockchain technology, financial institutions enable faster, more secure, and cost-effective cross-border transactions. Blockchain’s decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces transactional complexities, resulting in faster settlement times and lower fees.
The healthcare industry, particularly in the United States, encounters obstacles of interoperability, regulatory compliance, and efficiency addressable with blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the management and sharing of medical records, by providing a secure, auditable, and efficient infrastructure. A blockchain infrastructure could manage electronic medical records, allowing patients to seamlessly transfer records to different providers and health systems without relying on the analog methods currently employed by many large health systems. Beyond the efficiency benefits, blockchain is already being investigated by the FDA for compliance purposes with the Drug Supply Chain Security Act, which requires that drugs be electronically traced from import to prescription in an interoperable manner.
The transactions and record-keeping challenges prominent in the real estate industry have the potential to be solved with blockchain technology. Leveraging blockchain’s decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining processes and reducing complexities. Furthermore, blockchain enhances security, trust, and regulatory compliance by providing a tamper-resistant and immutable record of property transactions.
Blockchain technology holds immense aptitude for various industries, transcending limitations to provide benefits across sectors. While its applications are not exclusive to any particular field, organizations can gain strategic advantages by embracing blockchain technology, particularly in financial services, supply chain healthcare, and real estate industries.
Blockchain Use-Cases
The benefits of blockchain are clear with many organizations across sectors already implementing blockchain infrastructure across various operations. As it stands now, blockchain is improving sustainability, ensuring supply chain providence, and securely managing public sector data. In the following section, we will explore three specific use cases pioneered by the World Bank, Walmart, and the Estonian government accompanied by the advantages provided by each system.
Chia Network partnered with the World Bank to develop a blockchain-based solution to garner increased support from institutional investors for climate-friendly projects in emerging markets. Currently, blockchain technology is deployed to enable carbon market data integrity, transparency, and efficiency across organizations and countries.
By utilizing blockchain technology in this way, the process of purchasing carbon offset credits is drastically simplified, bringing us one step closer to a carbon-neutral and sustainable world, while also investing in countries most threatened by climate change.
By leveraging Blockchain technology and Hyperledger Fabric, Walmart is revolutionizing the food supply chain ecosystem with enhanced transparency and traceability. By virtue of blockchain integration, employees can easily track product origins and current storage locations with a simple scan.
This technology drastically reduces the time it takes to trace food origins, streamlining operations and reducing paper and food waste. Furthermore, automation and enhanced transparency accelerate the supply chain, benefiting Walmart and its customers by providing quicker access to goods and services.
The KSI blockchain, implemented in Estonia, is a robust system that ensures data integrity and security by storing all citizen data on a distributed, public blockchain. KSI allows citizens to securely access and control their public sectors data, such as health records and government documents, empowering individuals to interact with public services while safeguarding their privacy.
For the government, the KSI blockchain enhances efficiency, transparency, and trust in data management, facilitating streamlined processes, reducing bureaucracy, and minimizing the risk of fraud and corruption. Estonia’s KSI blockchain benefits citizens and the government by fostering secure data management, empowering citizens, and improving public service delivery.
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the evident advantages of blockchain technology and actively adopting it within their operations. The current blockchain implementation by the World Bank, Walmart, and Estonia highlights the technology’s broad array of utility and benefits, specifically for sustainability, supply chain integrity, and secure data management.
In subsequent pieces, we will explore in greater detail the technical mechanisms allowing a blockchain to function, general applications for blockchain technology, and active use cases leveraging blockchain technology.